De-dollarization – The Global Movement towards Monetary Independence
Posted on: June 19, 2023 | By: M Vaseem Sheikh, Head – Financial Institutional Sales, Federal Bank<br> Anudeb Das Mahapatra, RM – Financial Institutional Sales, Federal Bank
De-dollarization
Transition away from US Dollars – Not in the near future but warrants a thought on preparation
The Global Movement Towards Monetary Independence
Introduction
The global economy has been dominated by the US dollar for decades, with many countries using it as their primary reserve currency. However, in recent years, there has been a growing movement towards de-dollarization, a term used to describe the shift away from the dollar and towards other currencies or alternative payment systems. This movement is motivated by various factors, including concerns about US economic and political power, the desire for monetary independence, and the need to protect against currency volatility. In this article, we will explore the concept of de-dollarization, its implications for the global economy, and the challenges and opportunities it presents.
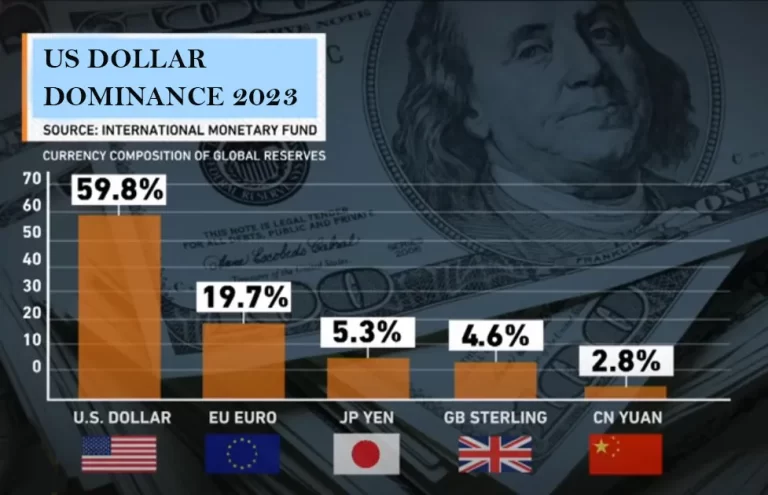
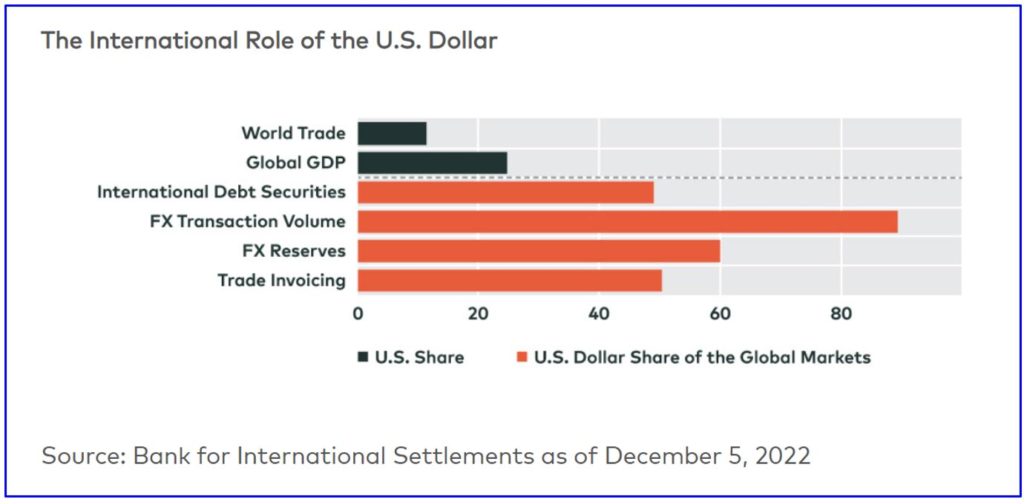
What is de-dollarization, and why is it important?
De-dollarization refers to the process of reducing or eliminating the use of the US dollar as a primary reserve currency and its replacement with other currencies or payment systems. This trend is driven by various factors, including concerns about the US economy and political power, currency volatility, and the need for monetary independence.
One of the main reasons that de-dollarization is important for countries and even global financial institutions is the potential risks associated with relying heavily on the US dollar. The US economy is the world’s largest, which means that fluctuations in the value of the dollar can have significant economic repercussions for the rest of the world. Moreover, the use of the dollar as a primary reserve currency and settlement currency creates a situation where the US has a significant amount of control over the global economy, which can lead to geopolitical tensions and challenges.
Furthermore, many countries are looking for alternatives to the US dollar to reduce the risks associated with currency fluctuations. Maintaining economic stability and protecting against currency volatility are essential goals for countries, and a diversified reserve currency portfolio is one way of achieving those goals.
Overall, de-dollarization is an important trend that reflects the desire for greater monetary independence and a more balanced global economy. While there are challenges associated with moving away from the US dollar, there are also opportunities for countries to develop new financial networks, improve financial stability, and build stronger economic relationships with other countries.
The history of monetary independence movements
The movement towards monetary independence is not a new phenomenon. For centuries, countries have sought to reduce their dependence on other nations’ currencies and establish their own economic foundations.
One of the earliest examples of a monetary independence movement dates to the 18th century, when the American colonies sought to break free from Britain’s control over their currency. In the years leading up to the Revolutionary War, colonial governments issued their own paper currency in an effort to reduce their reliance on British currency. This move towards monetary independence played a significant role in the colonies’ fight for freedom.
In more recent times, countries such as China and Russia have been vocal advocates for de-dollarization. Both countries have been working to reduce their dependence on the US dollar and have been boosting their gold reserves as a safeguard against currency fluctuations.
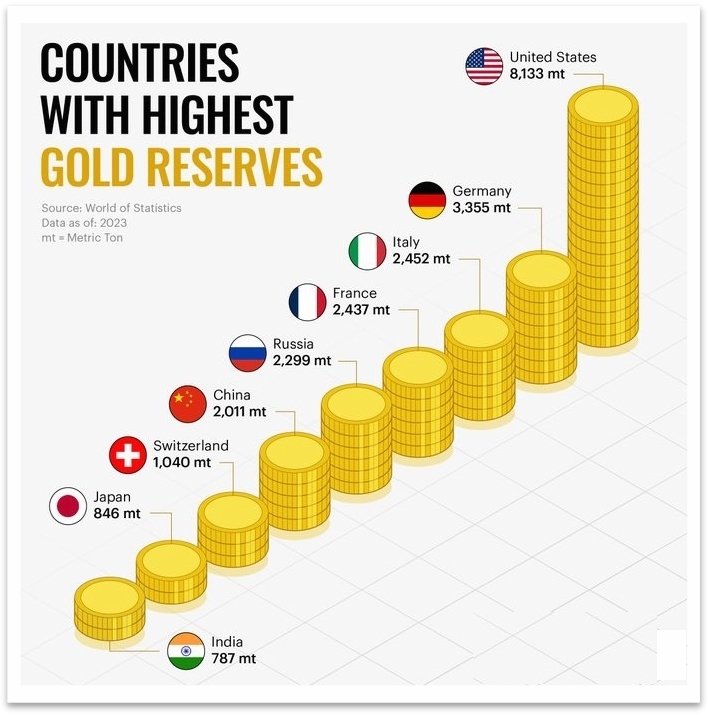
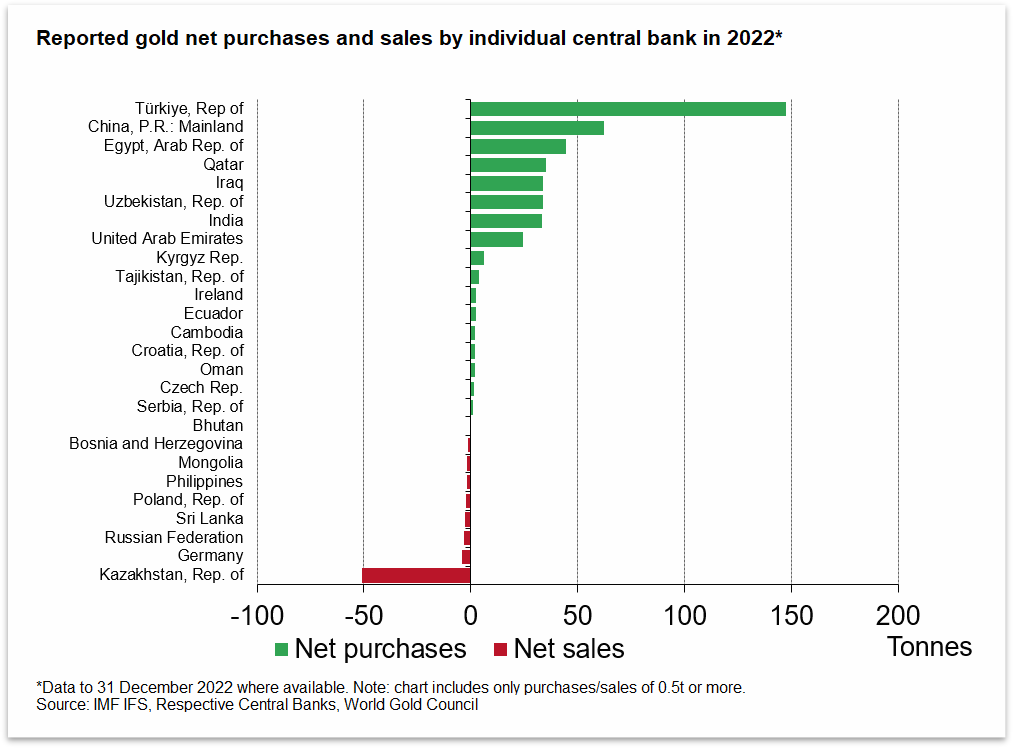
Another driving force behind the movement towards monetary independence has been the rise of cryptocurrency. Bitcoin and other digital currencies have given individuals and businesses a new way to conduct transactions and store value outside of traditional banking systems. While the long-term impact of cryptocurrency remains uncertain, many see it as a potential tool for achieving greater monetary independence.
Overall, the history of monetary independence movements shows that the desire for economic self-sufficiency is a powerful force. As global economic and political realities continue to evolve, it is likely that we will see more countries and individuals seeking to reduce their reliance on traditional currencies and financial institutions. De-dollarization may just be the beginning of a larger movement towards greater monetary autonomy
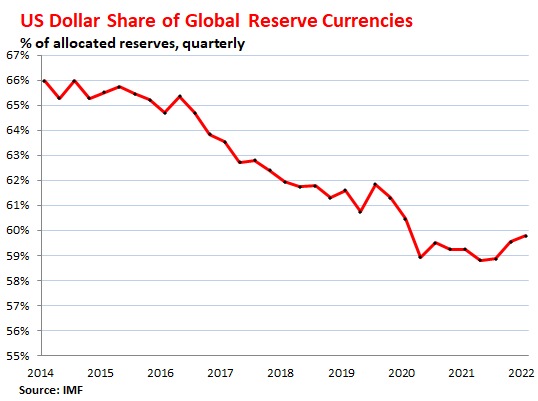
The benefits of de-dollarization for countries and businesses
De-dollarization, or reducing dependence on the US dollar, can bring several benefits for countries and businesses. Here are a few of them:
Reduced vulnerability to currency fluctuations: One of the major benefits of de-dollarization is that it reduces a country’s vulnerability to currency fluctuations. When a country relies heavily on the US dollar, any fluctuations in the value of the dollar can have a significant impact on its economy. De-dollarization allows countries to diversify their reserves and reduce this vulnerability.
Increased sovereignty: De-dollarization can also increase a country’s economic sovereignty. By reducing its reliance on the US dollar, a country can have greater control over its own economic policies and reduce the influence of external factors.
Greater economic stability: De-dollarization can also lead to greater economic stability. Countries that rely heavily on the US dollar are more vulnerable to economic shocks and crises, as they are often tied to the global economic system. De-dollarization can help countries insulate themselves from these shocks and promote more stable economic growth.
New opportunities for trade: De-dollarization can also create new opportunities for trade. By reducing reliance on the US dollar, countries can explore new trade partnerships and reduce barriers to trade with other nations. This can help to promote economic growth and diversify a country’s economy.
Overall, de-dollarization can bring several benefits for countries and businesses. As global economic and political realities continue to evolve, it is likely that we will see more countries and individuals seeking to reduce their reliance on traditional currencies and financial institutions.

Challenges and risks associated with de-dollarization
While de-dollarization can bring many benefits, there are also several challenges and risks associated with the movement towards monetary independence. Here are a few of them:
Currency volatility: While reducing reliance on the US dollar can reduce vulnerability to currency fluctuations, it can also introduce new currency risks. Choosing the right currencies to diversify into can be a challenge, as exchange rates can be volatile and unpredictable.
Increased transaction costs: Transactions that involve multiple currencies can be more complex and more expensive. This can be a particular challenge for small businesses and developing countries.
Difficulty accessing global financial markets: De-dollarization may make it more difficult for countries to access global financial markets, particularly if they are seen as high-risk or if their currencies are not widely accepted.
Political risks: De-dollarization can be perceived as a political move, and it may have implications for relationships with the United States and other countries. Countries that de-dollarize may face backlash or diplomatic challenges, particularly if the move is seen as a threat to US economic or political dominance.
Potential impact on global trade: De-dollarization can have implications for global trade, particularly if it leads to the fragmentation of international financial systems. This could potentially lead to higher trade barriers and reduced trade volumes.
While de-dollarization can bring many benefits, it is important to carefully consider the risks and challenges associated with the process. Countries and businesses must weigh the potential benefits against the potential costs and develop strategies to manage the risks associated with a move towards monetary independence.
How countries are embracing de-dollarization
Countries around the world are increasingly embracing de-dollarization as a means of achieving monetary independence. Here are some examples of countries that are actively pursuing de-dollarization:
China: China has taken a number of steps towards de-dollarization, including promoting the use of its own currency (the yuan) in international trade and investment. The country has also reduced its holdings of US Treasury bonds in recent years.
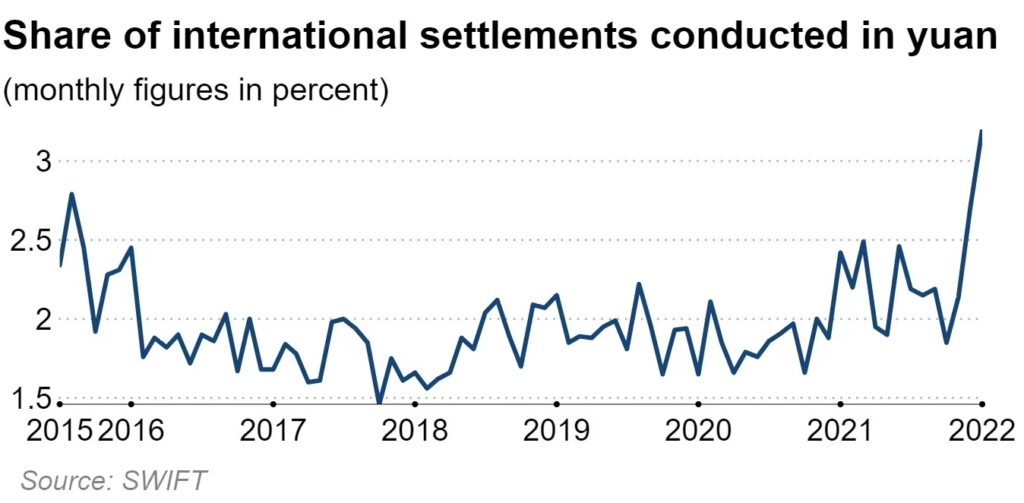
Russia: Like China, Russia has been promoting the use of its own currency (the ruble) in international trade. The country has also been reducing its holdings of US Treasury bonds and has been increasing its gold reserves.
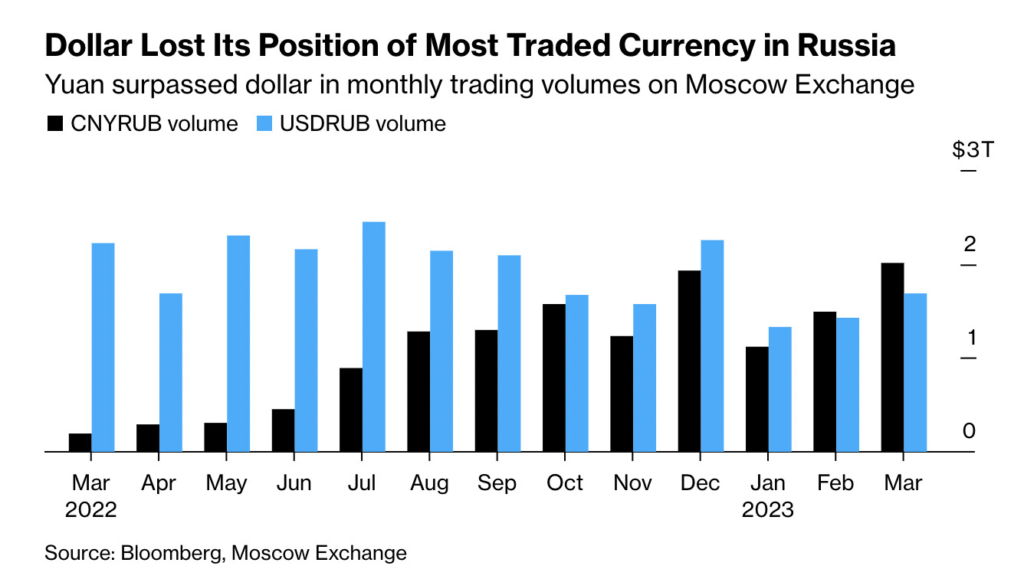
Iran: Iran has been actively pursuing de-dollarization in response to US sanctions. The country has been seeking to switch to alternative currencies, such as the euro and the yuan, in its international trade.
Venezuela: Venezuela has been pursuing de-dollarization as a means of reducing its dependence on the US dollar, particularly in response to US sanctions. The country has been exploring the use of alternative cryptocurrencies as well as other currencies such as the yuan.
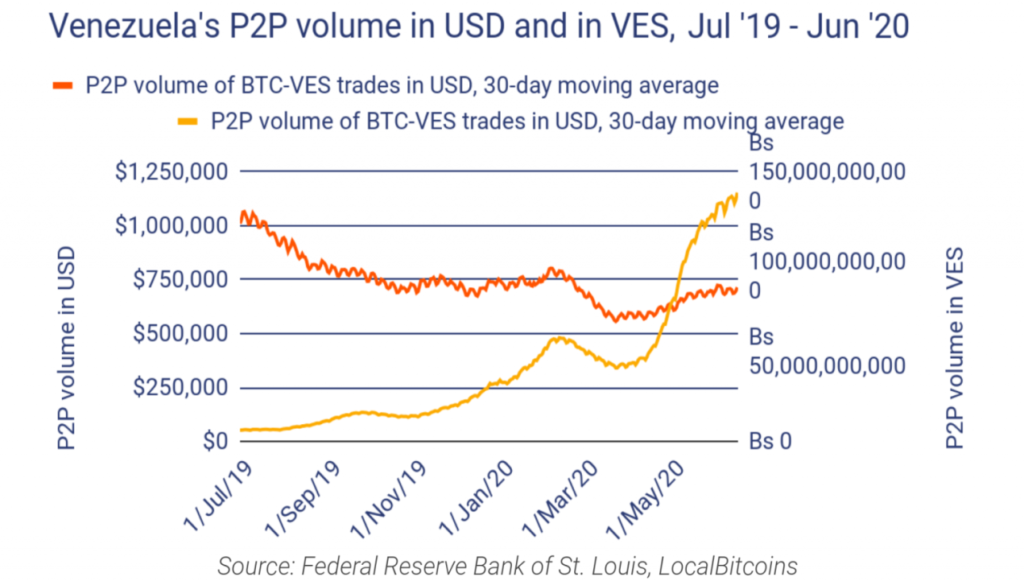
Turkey: Turkey has also been pursuing de-dollarization in response to US sanctions. The country has been seeking to increase the use of its own currency (the lira) in international trade and has been exploring alternative sources of financing.
India: India announced its new international trade policy, which allows the use of rupees in transactions with countries suffering from a lack of dollars or currency challenges. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), India’s central bank, approved in July 2022 to allow the settlement of foreign trade in rupees. This step was taken to promote internationalization of Indian Rupee (INR).
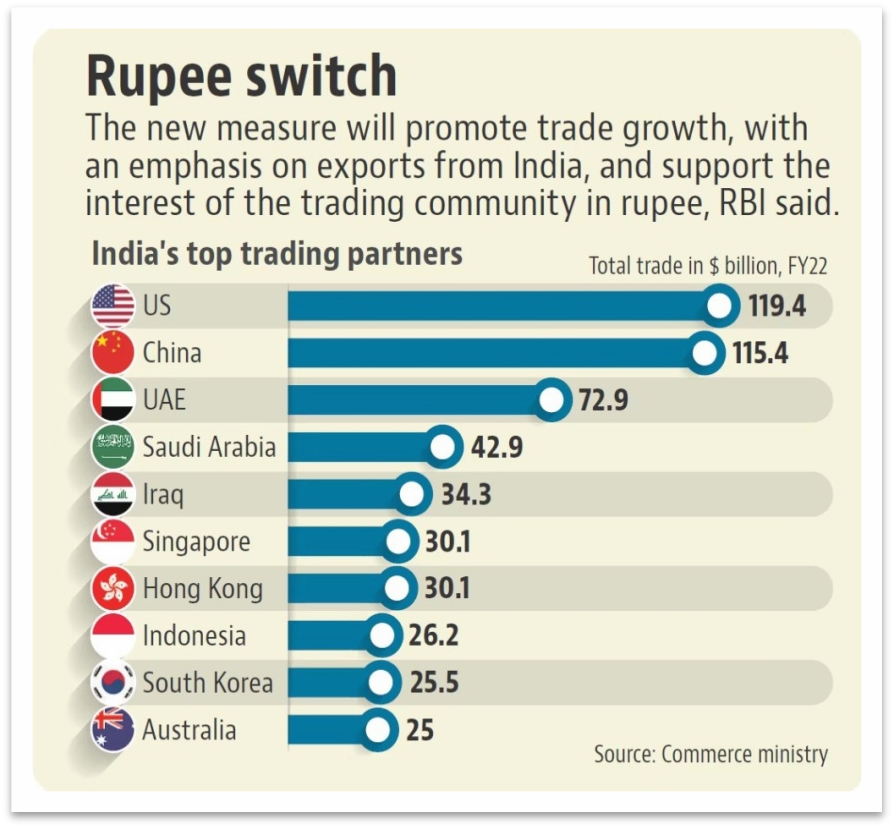
As these examples demonstrate, de-dollarization is an increasingly popular strategy among countries seeking greater monetary independence. However, each country faces its own unique challenges and risks in pursuing this strategy, and the success of de-dollarization efforts will depend on a complex interplay of political, economic, and geopolitical factors.
What businesses can do to prepare for a de-dollarized future
As more countries embrace de-dollarization, businesses must also prepare for a future without the US dollar as the dominant currency. Here are some steps businesses can take to prepare for a de-dollarized future
Diversify currency holdings: Businesses should consider diversifying their currency holdings to include alternative currencies such as the Yuan, Euro, Swiss Franc or INR. This reduces their dependence on the US dollar and mitigates the risks associated with fluctuations in the value of any one currency.
Hedge against currency risks: Hedging against currency risks involves taking steps to protect against fluctuations in exchange rates. Businesses can do this by using financial instruments such as futures contracts, currency options, or forward contracts.
Establish local currency bank accounts: To reduce reliance on the US dollar, businesses can establish local currency bank accounts in the countries where they operate. This reduces the need to convert funds into US dollars and minimizes exposure to currency risks.
Adapt to new payment methods: As other currencies become more widely used, businesses must adapt to new payment methods. This could include accepting payments in alternative currencies, using cryptocurrency, or implementing blockchain-based payment systems.
Develop new trade relationships: As the global monetary landscape shifts, it is important for businesses to establish new trade relationships with countries that are embracing alternative currencies. This could mean exploring new markets or forging partnerships with suppliers and customers in de-dollarized economies.
In conclusion, businesses that prepare themselves for a de-dollarized future are likely to be in a better position to adapt to the changes ahead and can remain competitive in an increasingly complex global economy.
Conclusion: The Future of global monetary independence
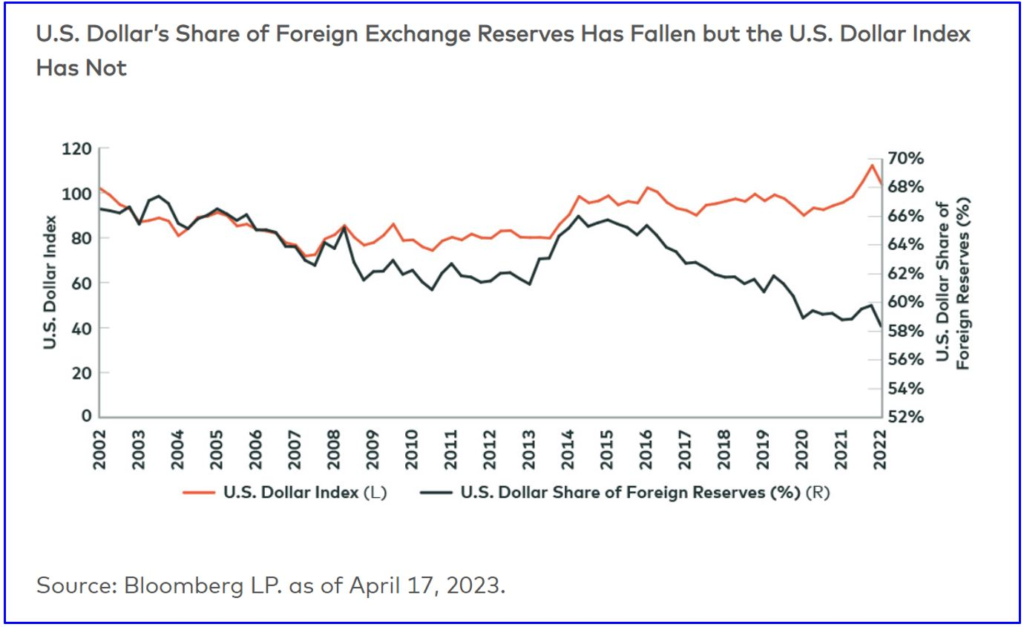
In conclusion, de-dollarization is a global movement towards monetary independence that is gaining traction in many countries. The dominance of the US dollar as the world’s reserve currency is being challenged by the rise of alternative currencies and the growing power of emerging economies. Businesses that prepare themselves for a de-dollarized future are more likely to thrive in a complex and dynamic global economy.
To prepare for this future, businesses can take practical steps such as diversifying currency holdings, hedging against currency risks, establishing local currency bank accounts, adapting to new payment methods, and developing new trade relationships. By doing so, they can reduce their dependence on the US dollar and minimise exposure to currency risks while also taking advantage of new opportunities in emerging markets.
Overall, the future of global monetary independence is uncertain, but one thing is clear: businesses that are flexible, adaptable, and forward-looking will be better prepared to succeed in the years ahead. With the right strategies and a willingness to embrace change, they can thrive in a world where the US dollar is no longer the dominant currency.








